UPS capacity utilization UPS power supply provides reliable power for equipment. UPS power supply can ensure that in the case of sudden power failure, the equipment can work normally without accidents and related important data loss. In addition, under normal power supply conditions, UPS power supply has functions such as voltage stabilization, anti-interference, prevention of waveform distortion, and lightning protection.
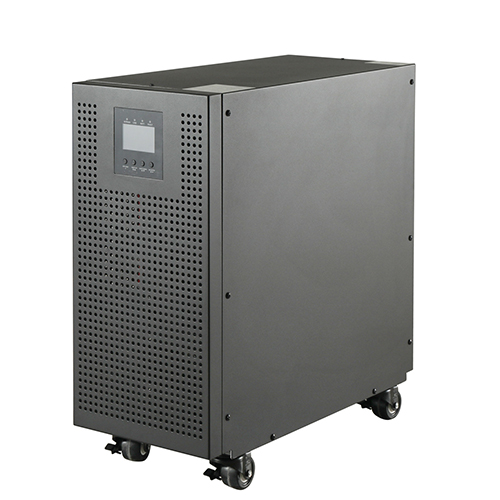

UPS usually consists of rectifier, battery, inverter, static switch and control system. Usually an online UPS is used. First, from the mains input to the adjustable DC power supply, the AC power supply is supplied by the battery and
The inverter then converts to stable, pure, high-quality AC power. Completely eliminate all power problems (voltage fluctuations, frequency fluctuations, harmonic distortion and various interferences) that may occur with the input power.
Due to the non-linear load of various switching power supplies and various printer loads of equipment in the computer room, the inrush current of these loads is very large. The UPS power supply capacity is too small, and the waveform distortion is prone to occur under heavy load for a long time, and the overcurrent and heavy load of the output final power supply equipment are likely to generate heat, and the system reliability is greatly reduced. For high-capacity UPS, it is generally recommended to control the capacity utilization between 0.6 and 0.8.
Whether the UPS has a high power factor. If the UPS load is an inductive load or a capacity load, a UPS with a full-bridge softswitch converter must be used. The UPS was born with the computer. The UPS is the peripheral equipment of the computer, the energy storage equipment and the inverter are the main components, and the power supply protection equipment with stable voltage and frequency output. Solve existing problems such as power failure, pressure, high voltage, surge, noise, etc., and make the computer system run more safely and stably. Currently widely used in computer, telecommunications, banking, securities, telecommunications, medical, industrial control and other fields.
 English
English
 Español
Español
 Português
Português
 русский
русский
 français
français
 日本語
日本語
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt
 Italiano
Italiano
 Nederlands
Nederlands
 ไทย
ไทย
 Polski
Polski
 한국어
한국어
 Svenska
Svenska
 magyar
magyar
 Malay
Malay
 বাংলা
বাংলা
 Dansk
Dansk
 Suomi
Suomi
 हिन्दी
हिन्दी
 Pilipino
Pilipino
 Türk
Türk
 Gaeilge
Gaeilge
 عربى
عربى
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 norsk
norsk
 اردو
اردو
 čeština
čeština
 Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά
 Українська
Українська
 Javanese
Javanese
 فارسی
فارسی
 தமிழ்
தமிழ்
 తెలుగు
తెలుగు
 नेपाली
नेपाली
 Burmese
Burmese
 български
български
 ລາວ
ລາວ
 Latine
Latine
 Қазақ
Қазақ
 Euskal
Euskal
 Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan
 slovenský
slovenský
 Македонски
Македонски
 Lietuvos
Lietuvos
 Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel
 Română
Română
 Slovenski
Slovenski
 Српски
Српски
 Беларус
Беларус


